If superannuation guarantee (“SG”) payments are paid late, that is after the 28th day from the quarter end, you are liable for the Superannuation Guarantee Charge (“SGC”). This involves lodging a form with the ATO and will include an interest and administration fee component.
Businesses that pay overtime – be aware!
Once your SG payment is made after the due date, the definition of “earnings” for SGC calculations changes to include overtime payments.
Normally superannuation is calculated on Ordinary Times Earnings (OTE). This includes several items relating to standard earnings, but excludes other items, for example, overtime payments.
However, when payments are made late, superannuation is required to be calculated on a salary or wages. This includes a broader range of earnings and includes items such as overtime.
On top of this, penalties can be applied up to 200% of the SGC shortfall along with interest charges.
Let’s look at some numbers show how serious this can be.
ABC Pty Ltd has 3 employees, earnings for the quarter as follows:
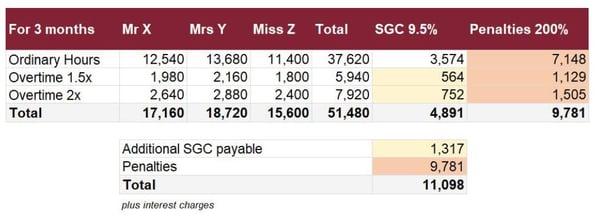
The above example shows how just by paying SG late of $3,574, you could end up with an additional $11,098 to pay. And this is just for one quarter!
You can see how this cost would increase substantially for employers who:
- Have staff that work large amounts of overtime
- Regularly pay their superannuation late
- Have larger numbers of employees
Given the ATO can audit your SG compliance for a 4 year period, it is critical you calculate and pay your superannuation on time.
If you have any concerns about complying with your SG obligations, please contact the Cutcher & Neale team.
Cutcher's Investment Lens | 14-18 April 2025
Cutcher's Investment Lens | 7 - 11 April 2025
The failed $3 million super tax: Division 296 is done… or is it?
Cutcher's Investment Lens - Update on Trump & Tariffs | 31 March - 4 April 2025
Liberation Day - April 2025 Snapshot




